Different types of baldness can affect both men and women, and understanding them is key to finding the right treatment. There are various causes of hair loss, ranging from genetics to lifestyle factors, and each type of baldness has its unique characteristics.
In this article, we’ll explore the different types of baldness, their causes, and available treatments. Whether you’re dealing with male pattern baldness, scarring alopecia, or another condition, it’s important to know your options for managing and treating hair loss.
We’ll also dive into effective solutions like minoxidil after hair transplant, which can help restore your hair and prevent further loss. Understanding the different types of baldness will help you take the first step toward healthier hair.
Understanding Baldness
Baldness, or hair loss, can occur in various forms and affect both men and women differently. It’s essential to distinguish between thinning hair and full baldness, as the causes and treatment options may differ.
The hair growth cycle plays a significant role in baldness. Hair goes through several phases: the anagen (growth) phase, the catagen (transition) phase, and the telogen (resting) phase.
Factors such as genetics, hormones, age, and even environmental influences like stress and nutrition can impact this cycle, leading to hair loss. In this section, we will explain the biology of hair growth and how it leads to different types of baldness.
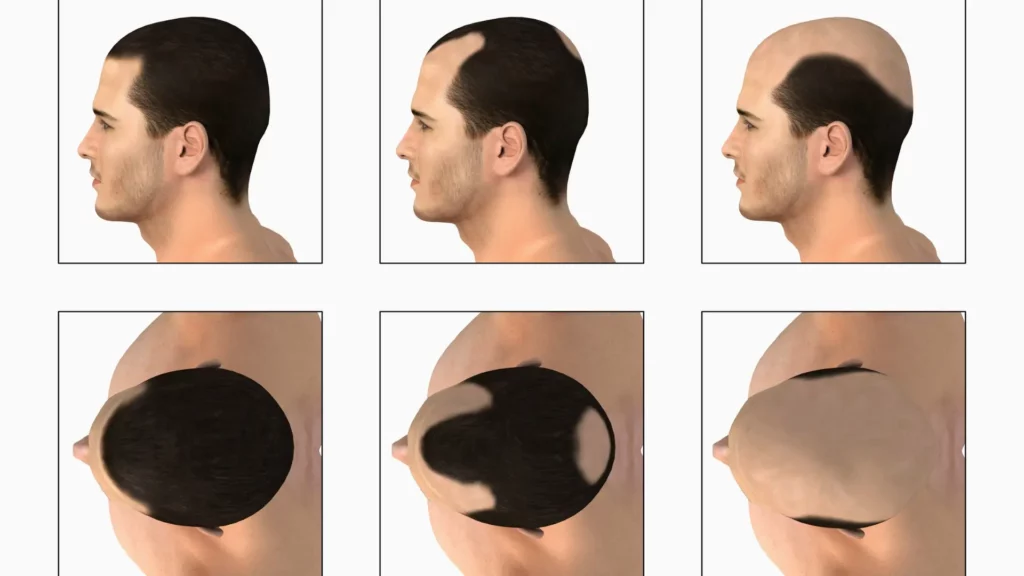
Different Types of Baldness
When dealing with hair loss, it’s essential to understand the different types of baldness to find the most effective treatment. Each condition has its causes, symptoms, and potential solutions. Below, we explore some of the most common forms of baldness and their treatments.
Androgenetic Alopecia (Male and Female Pattern Baldness)
One of the most common types of baldness is male pattern baldness, caused by genetics and exacerbated by hormonal factors like dihydrotestosterone (DHT). It typically starts with a receding hairline or thinning at the crown. In women, female pattern baldness causes diffuse thinning across the scalp. Treatments include minoxidil, finasteride, and hair transplant surgery, with minoxidil after hair transplant being a popular option to help maintain results.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder where the body’s immune system attacks the hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss. In severe cases, it can progress to alopecia totalis, where all scalp hair is lost, or alopecia universalis, which leads to complete body hair loss. Treatment options like corticosteroids, immunotherapy, and wigs can help manage the condition and promote hair regrowth.
Telogen Effluvium
Telogen effluvium is a temporary condition that causes the widespread thinning of hair across the scalp. It is often triggered by stress, illness, or hormonal changes. Once the underlying cause is addressed, hair usually regrows within several months, making telogen effluvium largely reversible.
Traction Alopecia
This type of baldness is caused by constant tension from tight hairstyles such as ponytails, braids, or buns. It leads to hair loss, particularly around the temples or hairline. Treatment involves avoiding tight hairstyles and switching to gentler hair care practices to allow regrowth.
Scarring Alopecia
Scarring alopecia, or cicatricial alopecia, occurs when inflammation permanently damages hair follicles, resulting in irreversible hair loss. Conditions like lupus, lichen planus, or folliculitis can cause this form of baldness. Treatment typically involves anti-inflammatory medications like corticosteroids to reduce further damage, but regrowth is not possible in affected areas without surgical interventions like hair transplants.
Anagen Effluvium
Anagen effluvium occurs when hair loss happens during the growth phase, often due to chemotherapy or radiation therapy. This results in rapid hair loss, but it is typically temporary. Once treatment ends, hair regrowth usually follows, although it may take several months.
Trichotillomania
Trichotillomania is a psychological condition where individuals have a compulsive urge to pull out their hair. This disorder can lead to noticeable bald patches. Treatment involves therapy, particularly cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), to help patients control this behavior and manage the condition effectively.
Diagnosing Baldness
When experiencing hair loss, it’s crucial to seek a professional diagnosis to understand which of the different types of baldness may be affecting you. A dermatologist or trichologist will assess the pattern and severity of your hair loss by examining the scalp and hair closely.
They will also inquire about your medical history, lifestyle, and family history to determine potential causes of your baldness. Identifying whether your condition is related to male pattern baldness, female pattern baldness, or conditions like alopecia areata can help in choosing the appropriate treatment.
Diagnosing different types of baldness typically involves several tests. Blood tests may be performed to check for underlying issues like hormonal imbalances or nutritional deficiencies.
A scalp biopsy could be needed if there is suspicion of an autoimmune disorder, such as scarring alopecia, which requires targeted treatment. Furthermore, a hair pull test helps assess the shedding rate, revealing whether your hair loss is temporary or more chronic.
By thoroughly evaluating these factors, your healthcare provider can determine whether your baldness is caused by genetics, medical conditions, or external stressors. This will guide the development of a tailored treatment plan to address the underlying cause and help you manage your hair loss effectively.
Treatment Options for Baldness
When dealing with hair loss, exploring the different types of baldness and their specific causes is key to selecting the right treatment. Whether you’re experiencing male pattern baldness, female pattern baldness, or alopecia areata, understanding the treatment options available can help you take control of your hair restoration journey.
Medications
Minoxidil is a popular over-the-counter topical solution that stimulates hair growth, particularly for male pattern baldness. Finasteride, an oral medication, is effective in blocking DHT and is commonly used for male pattern baldness. Corticosteroids are used for alopecia areata to reduce inflammation and promote hair regrowth.
Hair Restoration Procedures
Hair transplant surgery is a permanent solution for male and female pattern baldness. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) Therapy and Laser Therapy (LLLT) are non-invasive options that can stimulate hair follicles and promote regrowth, especially in early stages of hair loss.
Lifestyle Changes and Natural Remedies
A balanced diet, stress management, and herbal supplements like saw palmetto can help slow down hair loss. These changes are particularly helpful in managing telogen effluvium and preventing male pattern baldness.
These treatment options address the root causes of different types of baldness, offering effective solutions for regrowth.
Ways of Preventing Baldness
While not all types of baldness are preventable, taking proactive steps can minimize hair loss and promote healthy hair.
Maintaining a Healthy Diet
A well-balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and minerals like vitamins A, B, C, D, E, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids plays a vital role in supporting healthy hair. Nutrient-dense foods such as leafy greens, fish, eggs, and nuts help strengthen hair follicles and prevent hair loss associated with different types of baldness, including male pattern baldness.
Managing Stress
Chronic stress can contribute to hair loss, especially in conditions like telogen effluvium, where hair follicles prematurely enter the shedding phase. Regular exercise, mindfulness practices, and ensuring adequate rest can help manage stress levels and prevent stress-induced hair shedding, thus reducing the risk of various types of baldness.
Avoiding Tight Hairstyles
Tight hairstyles like ponytails, braids, or buns often lead to traction alopecia, a condition where hair loss occurs around the hairline or temples due to tension on the hair follicles. To prevent this, avoid tight hairstyles and opt for looser, more natural hairdos that reduce the stress on the scalp.
Using Gentle Hair Care Products
Harsh chemicals found in some shampoos, conditioners, and styling products can cause damage to hair and contribute to thinning. Using gentle, sulfate-free products and avoiding excessive heat styling can protect your hair from becoming brittle and breaking, which helps prevent the onset of different types of baldness.
Early Detection and Treatment
If you notice early signs of hair thinning or shedding, it’s essential to seek medical advice. Early intervention can help prevent the progression of conditions like male pattern baldness and alopecia areata. Treatments like minoxidil can slow down hair loss and promote regrowth, especially if they are started early.
Conclusion
In conclusion, different types of baldness require distinct approaches for diagnosis and treatment.
From scarring alopecia to male pattern baldness, each condition has unique causes and potential solutions. Whether you opt for medications like minoxidil after hair transplant or choose more permanent solutions like hair transplants, there are several ways to manage hair loss.
Understanding the underlying causes of your baldness is the first step toward regaining control over your hair. If you’re concerned about hair loss, consulting with a healthcare professional can help you explore the best treatment options tailored to your needs.














